As AI becomes significant in our lives, we know it’s way ahead in its computational abilities in many ways. We also share some similarities, given that AI is ultimately a derivative of our intelligence. The data it processes stems from the capabilities of our brains. Let’s explore the intersection of human and artificial intelligence, comparing and contrasting their concepts.
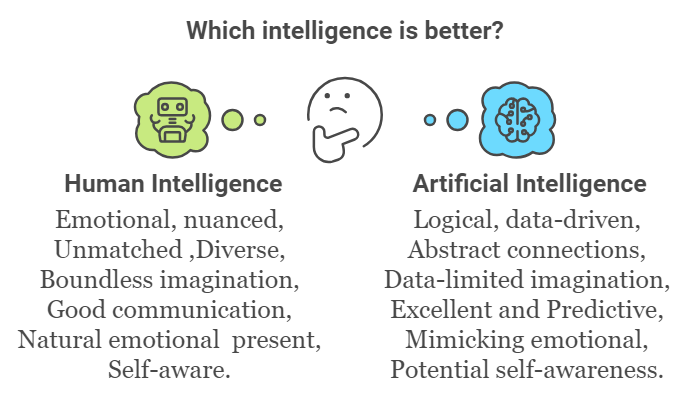
Defining Intelligence
Human Intelligence
At its core, Human Intelligence is the ability to learn, reason, and adapt to the environment. Intelligence evolved to help us survive. Although it is difficult to properly define intelligence, it broadly encapsulates these aspects.
- Problem Solving skills
- Creativity
- Imagination
- Communication
- Self-awareness.
- Emotional intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
AI is a field of computer science, which uses intelligence similar to humans to perform certain tasks. These tasks include learning from experience, understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, solving problems, making decisions, and demonstrating creativity.
- Machine Learning
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Computer Vision
- Robotics
- Neural Networks
How Do Humans and Machines Learn?
Human Learning
Humans learn by collecting data from experiences, trying novel things, failing, succeeding, taking relevant experience, and updating our memory. Neurons in our brains communicate with each other. Donald Hebb’s theory, “Neurons that fire together wire together,” captures the strengthening of neural connections as experiences repeat. The brain continuously adapts, stores new data, and deletes old information.
Machine Learning
AI learns through data, often in one of two ways:
- Supervised Learning: AI is trained on labeled data with known outcomes, using models like linear regression and decision trees.
- Unsupervised Learning: AI identifies patterns in data that are not labeled like through clustering.
Neural Networks
We have to talk about Neural Networks, if we are comparing our brain and artificial neurons right? Because Neural networks are a type of machine learning model inspired by the human brain’s structure. The brain’s adaptability allows humans to make decisions based on context and emotions, while AI relies on programmed logic and data.
How does a Neuron work?
The dendrites of a neuron receive a signal, which is usually a chemical signal that triggers a change in the neuron’s membrane and sends it to the axon, where it triggers an action potential. Only a sufficiently strong signal can trigger the action potential. Then this action potential travels along the axon to the synapse, where it is passed on to the next neuron. So if the neuron keeps receiving the same strong signal on and on again, the connection between them gets stronger and stronger.
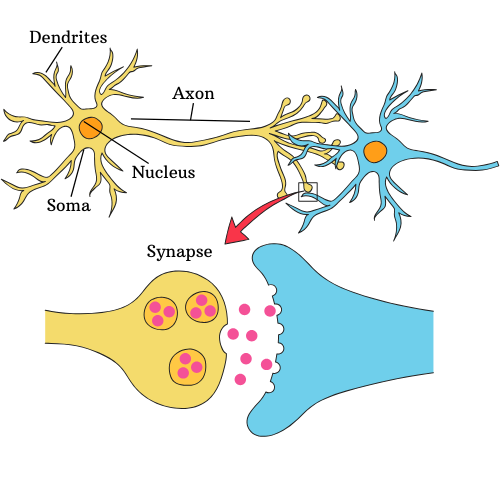
How does an AI neuron work?
An AI neuron is similar in concept, but instead of signals traveling physically like in biological neurons, it adjusts the numerical weights assigned to its inputs. These weights determine the strength of the connection. If the combined weighted input is strong enough, the AI neuron ‘activates’ and passes the signal forward. ( for more information: https://www.youtube.com/@3blue1brown)

The AI consists of neurons in layers:
- Input Layer: Receives initial data.
- Hidden Layers: Perform computations and extract features from the input.
- Output Layer: Produces final predictions or classifications.
Both humans and AI work through pattern recognition.
The structure of a human brain and a machine learning model both rely on networks. But the similarities end when we dive into their mechanics.
| Features | Human Brain | Artificial Neural Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | 86 billion neurons communicating via synapses | Fewer than 1,000 artificial neurons organized into layers |
| Learning Method | Experience-based learning | The decisions are contextually based and are very nuanced |
| Output | The decisions are contextual based and are very nuanced | Binary or categorical outputs |
| Energy Efficiency | ~20 watts | Can require hundreds to thousands of watts for training |
Processing Power and Energy Consumption
Human Brain
The human brain is estimated to perform about 1 exaFLOP (a billion billion calculations per second). It accomplishes this using only 20 watts of power, making it an energy-efficient powerhouse.
The brain processes simple tasks in about 20 milliseconds and can handle complex tasks by leveraging its 86 billion neurons. Although it may be slower in data-heavy tasks, its ability to handle emotions and context sets it apart.
AI Systems
In contrast, training large AI models, like GPT-3, consumes enormous energy. Running a single query on ChatGPT requires 2.9 watt-hours, compared to 0.3 watt-hours for a Google search .
AI, on the other hand, can process large amounts of data in milliseconds. For example, AI models like GPT-3 use up to 12 million GPUs to handle vast datasets in a fraction of the time it would take a human.
| Features | Human | AI |
|---|---|---|
| Processing speed | ~1 exaFLOP | Varies, often exceeds human speed |
| Task Complexity | can handle emotional and contextual tasks | good at data driven tasks |
| Parallel Processing | Limited by biological constraints | Extremely high with specialized hardware. |
Key Differences: Mapped
When we break down the different parameters that define intelligence, AI is making significant strides but hasn’t quite reached the full spectrum of human capabilities.
| Intelligence features | Human | AI |
|---|---|---|
| AI is rapidly improving communication, achieving high levels of proficiency in predicting words and interpreting context. | Well-rounded solutions take into consideration the emotional context and provides situationally appropriate responses. | Well-rounded solutions take into consideration the emotional context and provide situationally appropriate responses. |
| Creativity | Human creativity, from art and music to language, remains unmatched in its depth and complexity. | AI has surprised us by demonstrating creativity, showing that creativity can be seen as connecting abstract ideas in novel ways. |
| Imagination | Imagination is where humans truly stand out, with our ability to conceive of concepts far beyond data, often touching on consciousness. | AI’s “imagination” is limited to the data it’s trained on, lacking the abstract depth that humans possess. |
| Communication | While humans are excellent communicators, AI is becoming incredibly skilled at predicting and generating text, often with striking accuracy. | AI is advancing in emotional recognition, mimicking facial expressions and voice tones, but it still falls short of true emotional understanding. Progress in this area suggests that AI may improve shortly. |
| Emotional Intelligence | Humans excel at understanding and expressing emotions naturally. | The challenge lies in the potential of AI to reach this level with the development of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence). The implications of self-aware AI raise important questions. |
| Self-Awareness | Humans possess self-awareness, which is a key distinguishing factor. | The challenge lies in the potential of AI reaching this level with the development of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence). The implications of self-aware AI raise important questions. |
Let’s hear from you
[yop_poll id=”3″]
Conclusion
While AI has made impressive progress in problem-solving, creativity, and communication, areas where human intelligence continues to excel, are emotional intelligence, imagination, and self-awareness. But the gaps between these are also slowly closing. The speed at which the tech is accelerating gives us no time to comprehend the ethical and practical implications of these technologies. Maybe we are meant to evolve and co-exist and leverage the capabilities of the new technology to solve our most pressing questions. On a positive note, maybe our intelligence is seeking new horizons to stretch its capabilities.




Leave a comment